论文成果 / Publications
2025
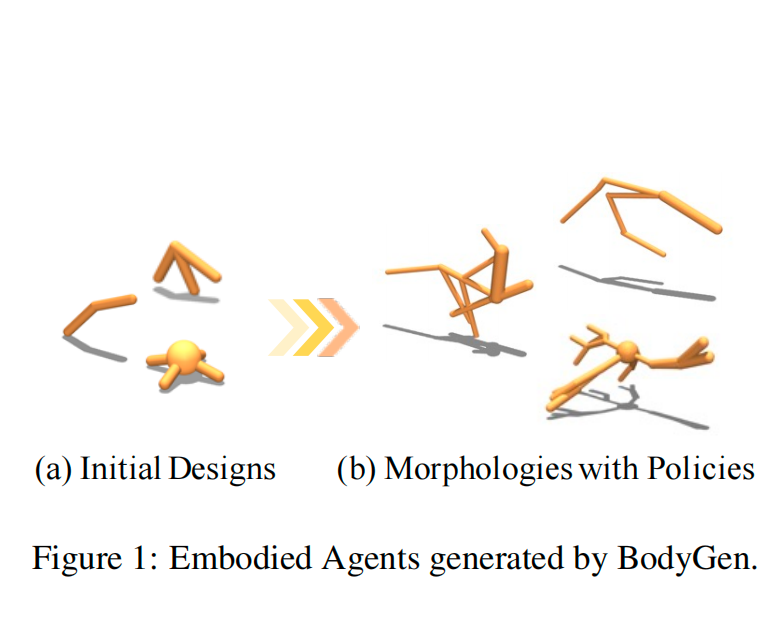
BodyGen: Advancing Towards Efficient Embodiment Co-Design
Abstract
Embodiment co-design aims to optimize a robot's morphology and control policy simultaneously. While prior work has demonstrated its potential for generating environment-adaptive robots, this field still faces persistent challenges in optimization efficiency due to the (i) combinatorial nature of morphological search spaces and (ii) intricate dependencies between morphology and control. We prove that the ineffective morphology representation and unbalanced reward signals between the design and control stages are key obstacles to efficiency. To advance towards efficient embodiment co-design, we propose BodyGen, which utilizes (1) topology-aware self-attention for both design and control, enabling efficient morphology representation with lightweight model sizes; (2) a temporal credit assignment mechanism that ensures balanced reward signals for optimization. With our findings, BodyGen achieves an average 60.03% performance improvement against state-of-the-art baselines. We provide codes and more results on the website: https://genesisorigin.github.io.
Understanding Users’ Perceptions and Expectations toward a Social Balloon Robot via an Exploratory Study
Abstract
We are witnessing a new epoch in embodied social agents. Most of the work has focused on ground or desktop robots that enjoy technical maturity and rich social channels but are often limited by terrain. Drones, which enable spatial mobility, currently face issues with safety and proximity. This paper explores a social balloon robot as a viable alternative that combines these advantages and alleviates limitations. To this end, we developed a hardware prototype named BalloonBot that integrates various devices for social functioning and a helium balloon. We conducted an exploratory lab study on users’ perceptions and expectations about its demonstrated interactions and functions. Our results show promise in using such a robot as another form of socially embodied agent. We highlight its unique mobile and approachable characteristics that harvest novel user experiences and outline factors that should be considered before its broad applications.
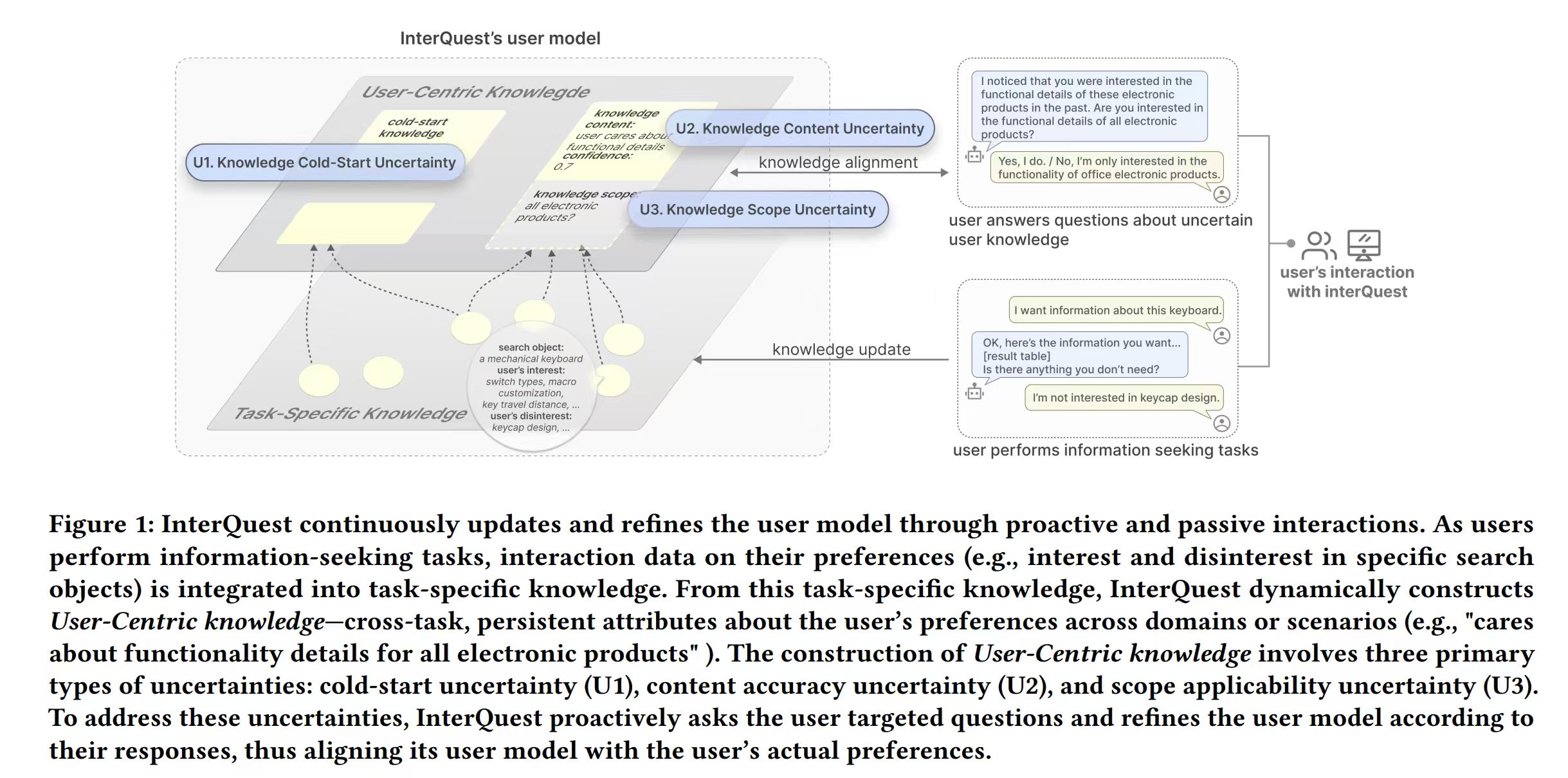
InterQuest: A Mixed-Initiative Framework for Dynamic User Interest Modeling in Conversational Search
Abstract
In online information-seeking tasks (e.g., for products and restaurants), users seek information that aligns with their individual preferences to make informed decisions. However, existing systems often struggle to infer users’ implicit interests—unstated yet essential preference factors that directly impact decision quality. Our formative study reveals that User-Centric Knowledge—cross-task persistent preference attributes of users (e.g., “user cares about functionality details for electronics”)—serves as a key indicator for resolving users’ implicit interests. However, constructing such knowledge from task-specific data alone is insufficient due to three types of uncertainties—cold-start limitation, content accuracy, and scope applicability—which require user-provided information for knowledge alignment. Based on these insights, we present InterQuest, an LLM-based conversational search agent that dynamically models user interests. InterQuest combines two strategies: (1) Dynamic User Knowledge Modeling, which infers and adjusts the content and scope of User-Centric Knowledge, and (2) Uncertainty-Driven Questioning, where InterQuest proactively asks questions to resolve knowledge uncertainties. A user study with 18 participants demonstrates that InterQuest outperforms the baselines in user interest inference, accuracy of user knowledge modeling, and the overall information-seeking experience. Additionally, our findings provide valuable design implications for improving mixed-initiative user modeling in future systems.
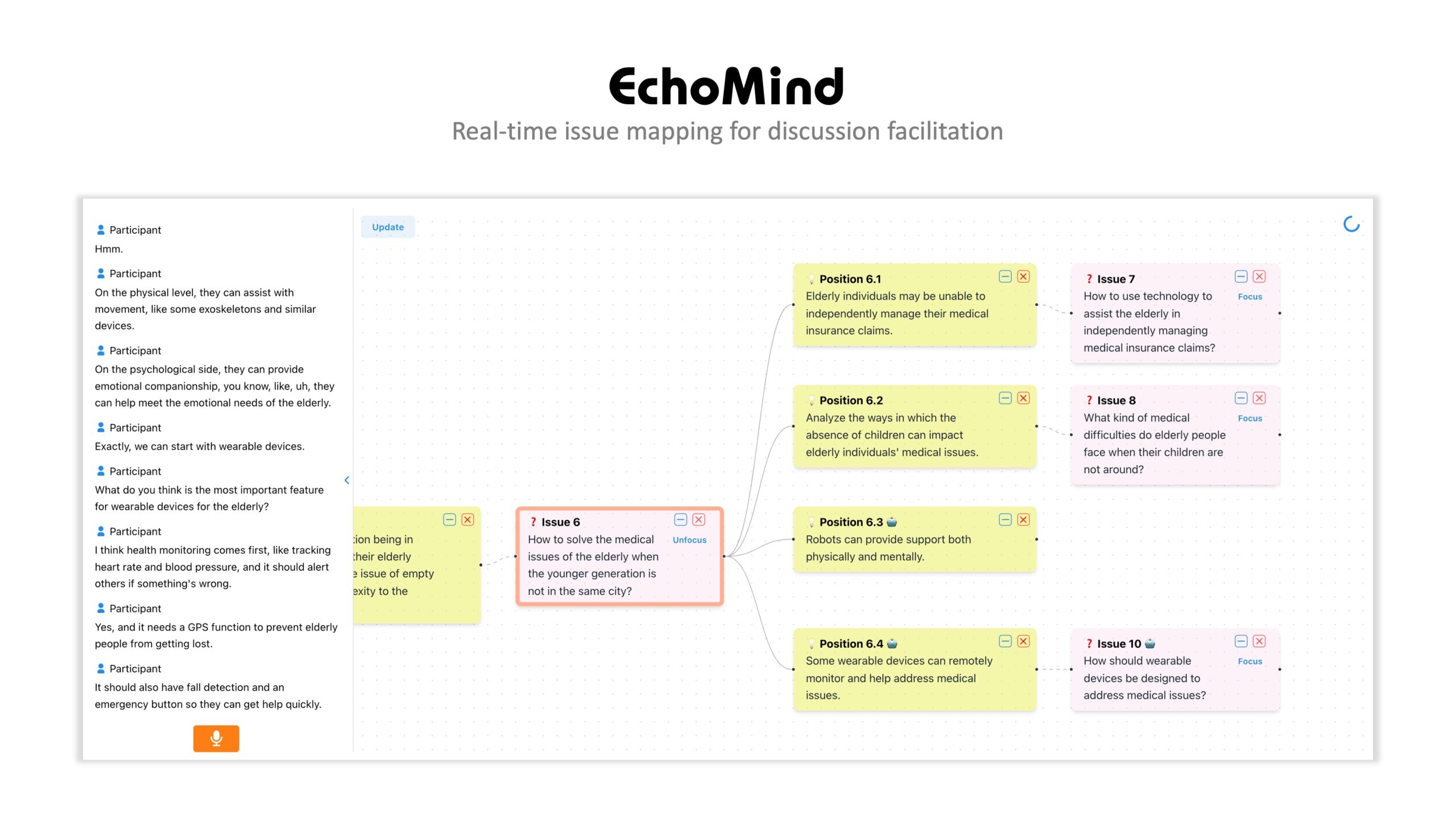
EchoMind: Supporting Real-time Complex Problem Discussions through Human-AI Collaborative Facilitation
Abstract
Teams often engage in group discussions to leverage collective intelligence when solving complex problems. However, in real-time discussions, such as face-to-face meetings, participants frequently struggle with managing diverse perspectives and structuring content, which can lead to unproductive outcomes like forgetfulness and off-topic conversations. Through a formative study, we explores a human-AI collaborative facilitation approach, where AI assists in establishing a shared knowledge framework to provide a guiding foundation. We present EchoMind, a system that visualizes discussion knowledge through real-time issue mapping. EchoMind empowers participants to maintain focus on specific issues, review key ideas or thoughts, and collaboratively
expand the discussion. The system leverages large language models (LLMs) to dynamically organize dialogues into nodes based on the current context recorded on the map. Our user study with four teams (N=16) reveals that EchoMind helps clarify discussion objectives, trace knowledge pathways, and enhance overall productivity. We also discuss the design implications for human-AI collaborative facilitation and the potential of shared knowledge visualization to transform group dynamics in future collaborations.
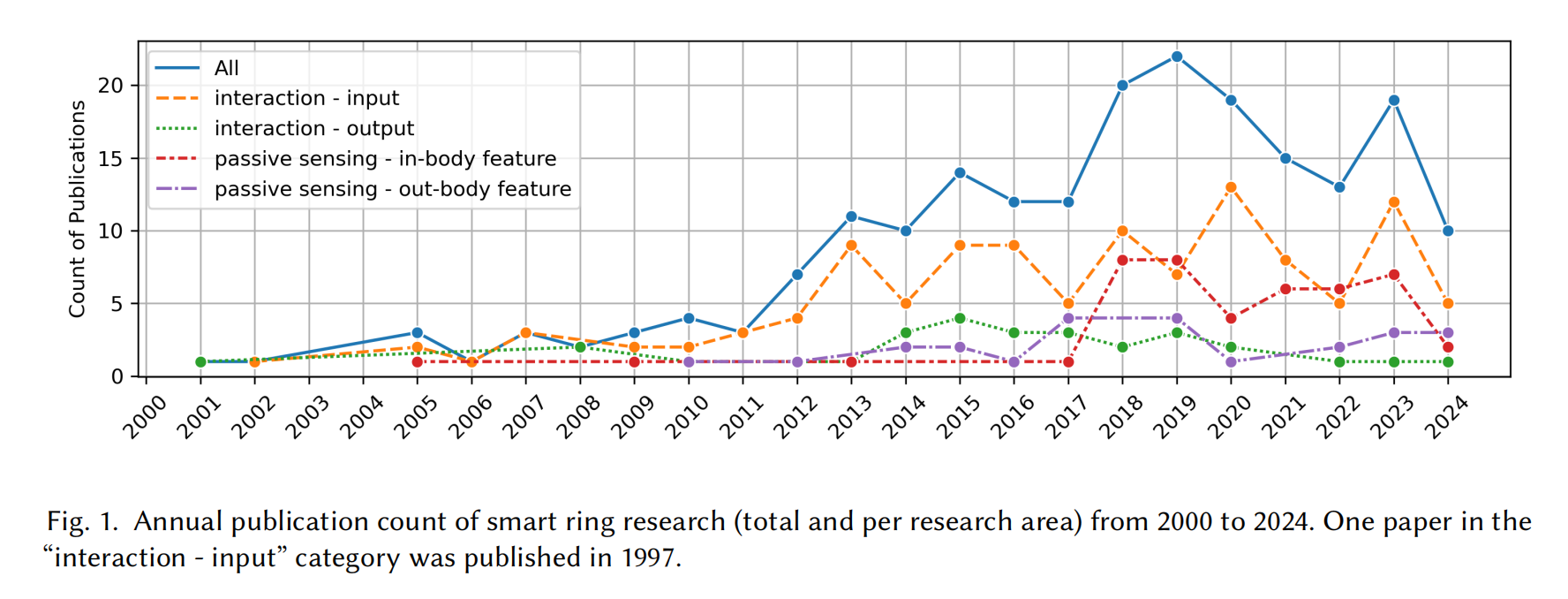
Computing with Smart Rings: A Systematic Literature Review
Abstract
A smart ring is a wearable electronic device in the form of a ring that incorporates diverse sensors and computing technologies to perform a variety of functions. Designed for use with fingers, smart rings are capable of sensing more subtle and abundant hand movements, thus making them a good platform for interaction. Meanwhile, fingers are abundant with blood vessels and nerve endings and accustomed to wearing rings, providing an ideal site for continuous health monitoring through smart rings, which combine comfort with the ability to capture vital biometric data, making them suitable for all-day wear. We collected in total of 206 smart ring-related publications and conducted a systematic literature review. We provide a taxonomy
regarding the sensing and feedback modalities, applications, and phenomena. We review and categorize these literatures into four main areas: (1) interaction - input, (2) interaction - output, (3) passive sensing - in body feature, (4) passive sensing - out body activity. This comprehensive review highlights the current advancements within the field of smart ring and identifies potential areas for future research.
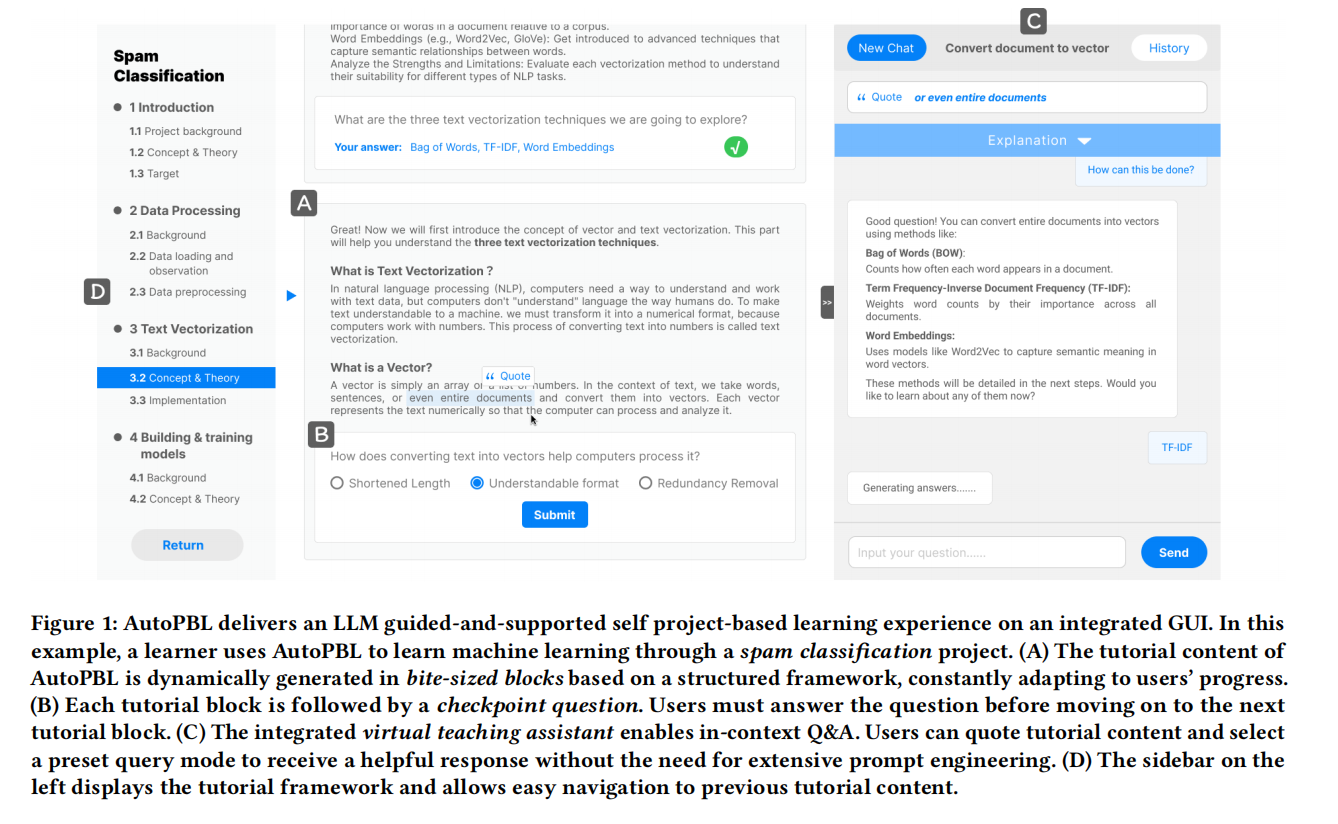
AutoPBL: An LLM-powered Platform to Guide and Support Individual Learners Through Self Project-based Learning
Abstract
Self project-based learning (SPBL) is a popular learning style where learners follow tutorials and build projects by themselves. SPBL combines project-based learning’s benefit of being engaging and
effective with the flexibility of self-learning. However, insufficient guidance and support during SPBL may lead to unsatisfactory learning experiences and outcomes. While LLM chatbots (e.g., ChatGPT)
could potentially serve as SPBL tutors, we have yet to see an SPBL platform with responsible and systematic LLM integration. To address this gap, we present AutoPBL, an interactive learning platform for SPBL learners. We examined human PBL tutors’ roles through formative interviews to inform our design. AutoPBL features an LLM-guided learning process with checkpoint questions and incontext Q&A. In a user study where 29 beginners learned machine learning through entry-level projects, we found that AutoPBL effectively improves learning outcomes and elicits better learning behavior and metacognition by clarifying current priorities and providing timely assistance.
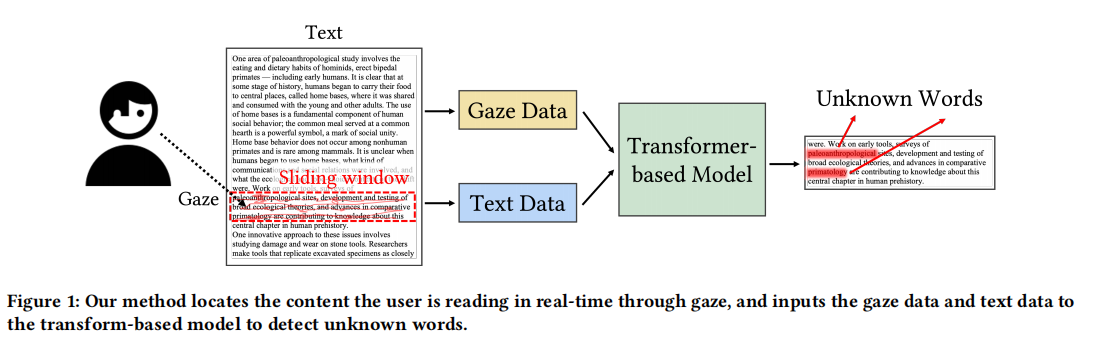
Unknown Word Detection for English as a Second Language (ESL) Learners using Gaze and Pre-trained Language Models
Abstract
English as a Second Language (ESL) learners often encounter unknown words that hinder their text comprehension. Automatically detecting these words as users read can enable computing systems
to provide just-in-time definitions, synonyms, or contextual explanations, thereby helping users learn vocabulary in a natural and seamless manner. This paper presents EyeLingo, a transformer based machine learning method that predicts the probability of unknown words based on text content and eye gaze trajectory in real time with high accuracy. A 20-participant user study revealed that our method can achieve an accuracy of 97.6%, and an F1-score of 71.1%. We implemented a real-time reading assistance prototype to show the effectiveness of EyeLingo. The user study shows improvement in willingness to use and usefulness compared to baseline methods.
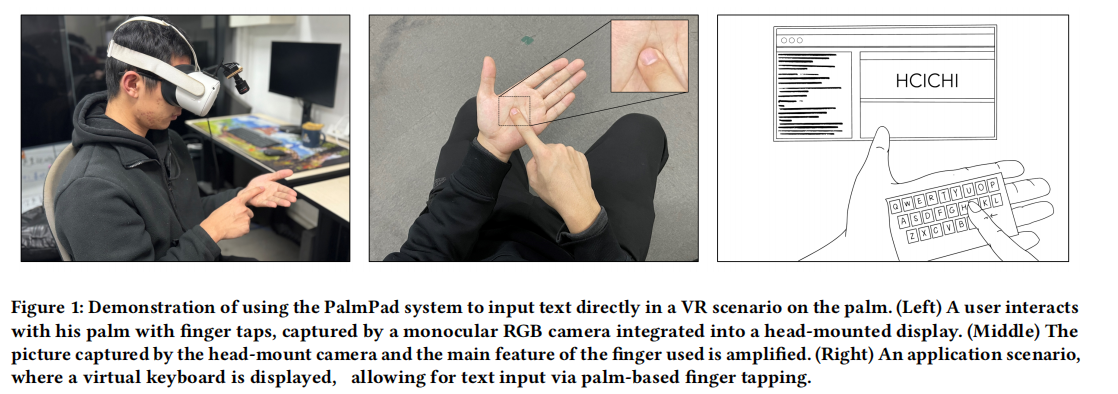
Palmpad: Enabling Real-Time Index-to-Palm Touch Interaction with a Single RGB Camera
Abstract
Index-to-palm interaction plays a crucial role in Mixed Reality(MR) interactions. However, achieving a satisfactory inter-hand interaction experience is challenging with existing vision-based hand tracking technologies, especially in scenarios where only a single camera is available. Therefore, we introduce Palmpad, a novel sensing method utilizing a single RGB camera to detect the touch of an index finger on the opposite palm. Our exploration reveals that the incorporation of optical flow techniques to extract motion information between consecutive frames for the index finger and palm leads to a significant improvement in touch status determination. By doing so, our CNN model achieves 97.0% recognition accuracy and a 96.1% F1 score. In usability evaluation, we compare Palmpad with Quest’s inherent hand gesture algorithms. Palmpad not only delivers superior accuracy 95.3% but also reduces operational demands and significantly improves users’ willingness and confidence. Palmpad aims to enhance accurate touch detection for
lightweight MR devices.
WritingRing: Enabling Natural Handwriting Input with a Single IMU Ring
Abstract
Tracking continuous 2D sequential handwriting trajectories accurately using a single IMU ring is extremely challenging due to the significant displacement between the IMU’s wearing position and the location of the tracked fingertip. We propose WritingRing, a system that uses a single IMU ring worn at the base of the finger to support natural handwriting input and provide real-time 2D trajectories. To achieve this, we first built a handwriting dataset using a touchpad and an IMU ring (N=20). Next, we improved the LSTM model by incorporating streaming input and a TCN network, significantly enhancing accuracy and computational efficiency, and achieving an average trajectory accuracy of 1.63mm. Real-time usability studies demonstrated that the system achieved 88.7% letter recognition accuracy and 68.2% word recognition accuracy, which reached 84.36% when restricting the output to words within a vocabulary of size 3000. WritingRing can also be embedded into existing ring systems, providing a natural and real-time solution for various applications.