论文成果 / Publications
2025
Communications of CCF | 人机协同中的交互式学习
Abstract
当我们将机器比作一位求学的学徒时,它获取基本常识或专业领域知识的主要途径无非是自学和请教老师。近期广受关注的大语言模型(Large Language Model,LLM)基于大规模数据集的预训练过程,如同学徒的“读万卷书”;而基于人类反馈的强化学习(RLHF)¹,则相当于学徒在课堂上向老师请教。最终,学徒毕业进入职场,但在与客户的交互中发现,从书本上和老师那里学到的知识要么不够用,要么不适用,以至于无法理解客户的具体需求和观点。这一例子揭示了以LLM为代表的机器智能在垂直领域中面临的现实瓶颈:在真实应用场景中,机器仍缺乏有效的学习路径来获取垂直领域知识或者个性化知识。那么,能否从以人为核心的人机交互(HCI)视角出发,突破这一瓶颈呢?本文将探讨一种新的机器学习范式——交互式学习,其核心在于通过人机自然交互过程,实现知识从用户到机器的高效传递,从而解决上述问题。我们将从人机协同的角度论证为什么交互式学习是克服现有模型训练局限、迈向通用智能的重要途径。
2024
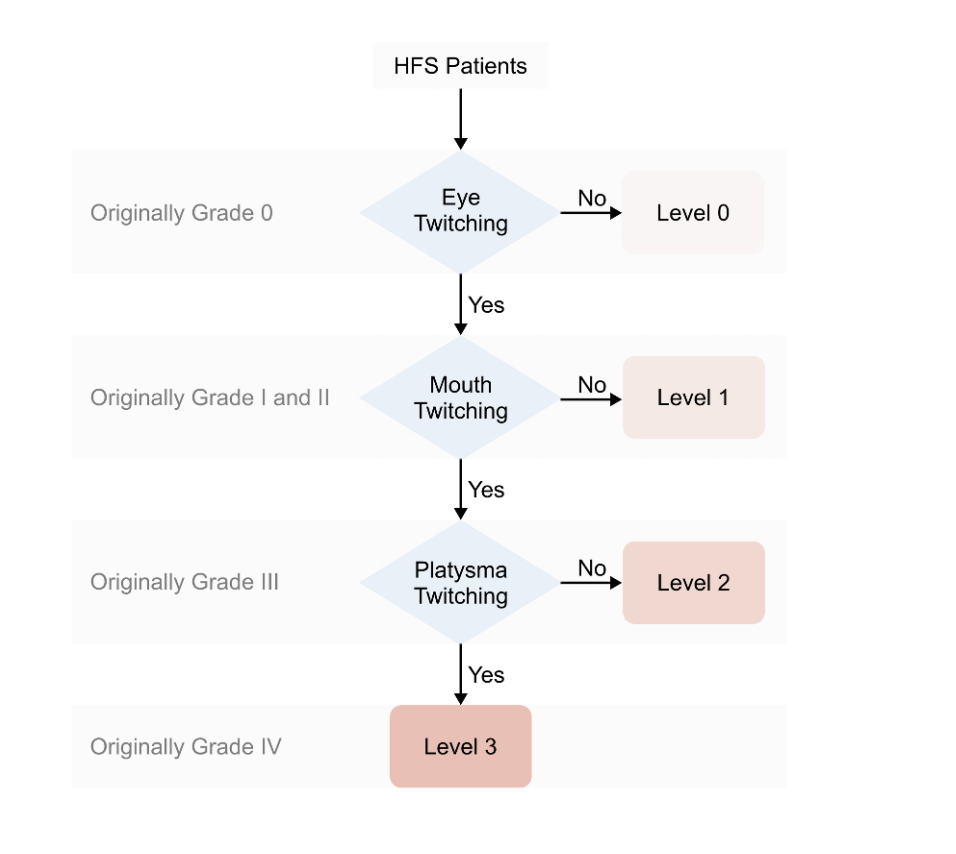
Automated Grading Hemifacial Spasm Using Smartphone Cameras
Abstract
Hemifacial spasm is a chronic neurological condition characterized by involuntary facial muscle contractions caused by nerve compression. While familiar to specialists, it is less known to the public and general practitioners, which can lead to difficulties in diagnosis and severity assessment, and even misdiagnosis. Consequently, patients are common to have a long medical history. However, long-term patients tend to have poorer outcomes following surgery, and one-third of patients experience a delayed cure during postoperative rehabilitation. Moreover, 4% of patients experience recurrence, highlighting the importance of early and accurate diagnosis as well as postoperative monitoring. In this paper, we collected a video dataset of 50 hemifacial spasm patients and 9 healthy adults. We identified three facial features from the videos to establish a novel grading system closely aligned with the medical standards, specifically the Cohen-Albert Grading System. We also developed algorithms capable of automatically grading hemifacial spasm using smartphone cameras based on facial keypoint detection. These algorithms were evaluated on the dataset, achieving an accuracy of 88% for detection and a mean absolute error of 0.42 for grading.
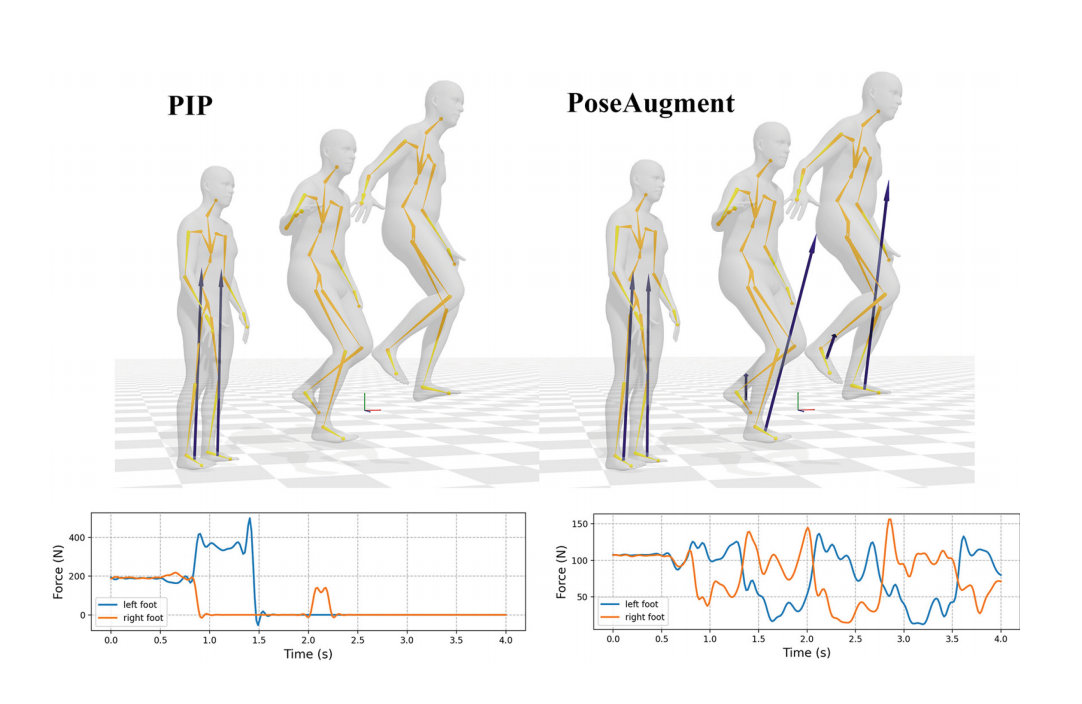
PoseAugment: Generative Human Pose Data Augmentation with Physical Plausibility for IMU-Based Motion Capture
Abstract
The data scarcity problem is a crucial factor that hampers the model performance of IMU-based human motion capture. However,
effective data augmentation for IMU-based motion capture is challenging, since it has to capture the physical relations and constraints of the human body, while maintaining the data distribution and quality. We propose PoseAugment, a novel pipeline incorporating VAE-based pose generation and physical optimization. Given a pose sequence, the VAE module generates infinite poses with both high fidelity and diversity, while keeping the data distribution. The physical module optimizes poses to satisfy physical constraints with minimal motion restrictions. High-quality IMU data are then synthesized from the augmented poses for
training motion capture models. Experiments show that PoseAugment outperforms previous data augmentation and pose generation methods in terms of motion capture accuracy, revealing a strong potential of our method to alleviate the data collection burden for IMU-based motion capture and related tasks driven by human poses.
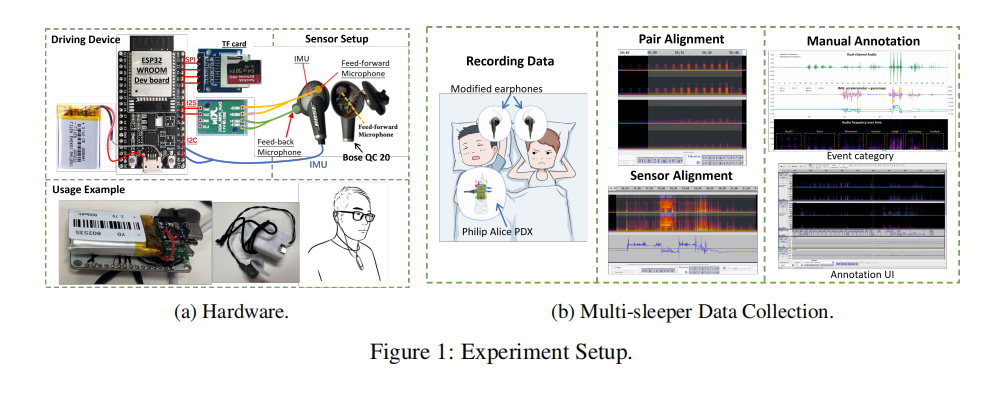
DreamCatcher: A Wearer-aware Sleep Event Dataset Based on Earables in Non-restrictive Environments
Abstract
Poor quality sleepcanbe characterized by the occurrence ofevents anging frombody movement to breathing impairment. Widely awailable earbuds equippedwith sensors (ako known as earables)can be combined with a sleep event de-tection algorithm to offer a convenientalemative to laboriousclinical tests forindividuals suffering from sleep disorders. Although warious solutions utilizingsuch devices have been proposed to detectsleepevents, they ignore the fact thatindividuas often share sleeping spaces with roommates or couples. To addressthis issue, we introduce DreamCatcher, the first publicly available dataset forwearer-aware sleep event algorithm development on earables. DreamCatcherencompasses eight distinctsleepevents, including synchronous dual-channel au-dioand motion data collected from 12 pairs (24 participants)toaling 210 hours(420 hourperson)with fine-grained label. We tested multiple benchmark mod-es on three tasks related to sleep event detection, demonstrating the usabilityand unique challenge of DreamCatcher. We hope thatthe proposed Dream-Catchercan inspire other researchers to further explore efficient wearer-awarehuman vocal activitysensing onearables.
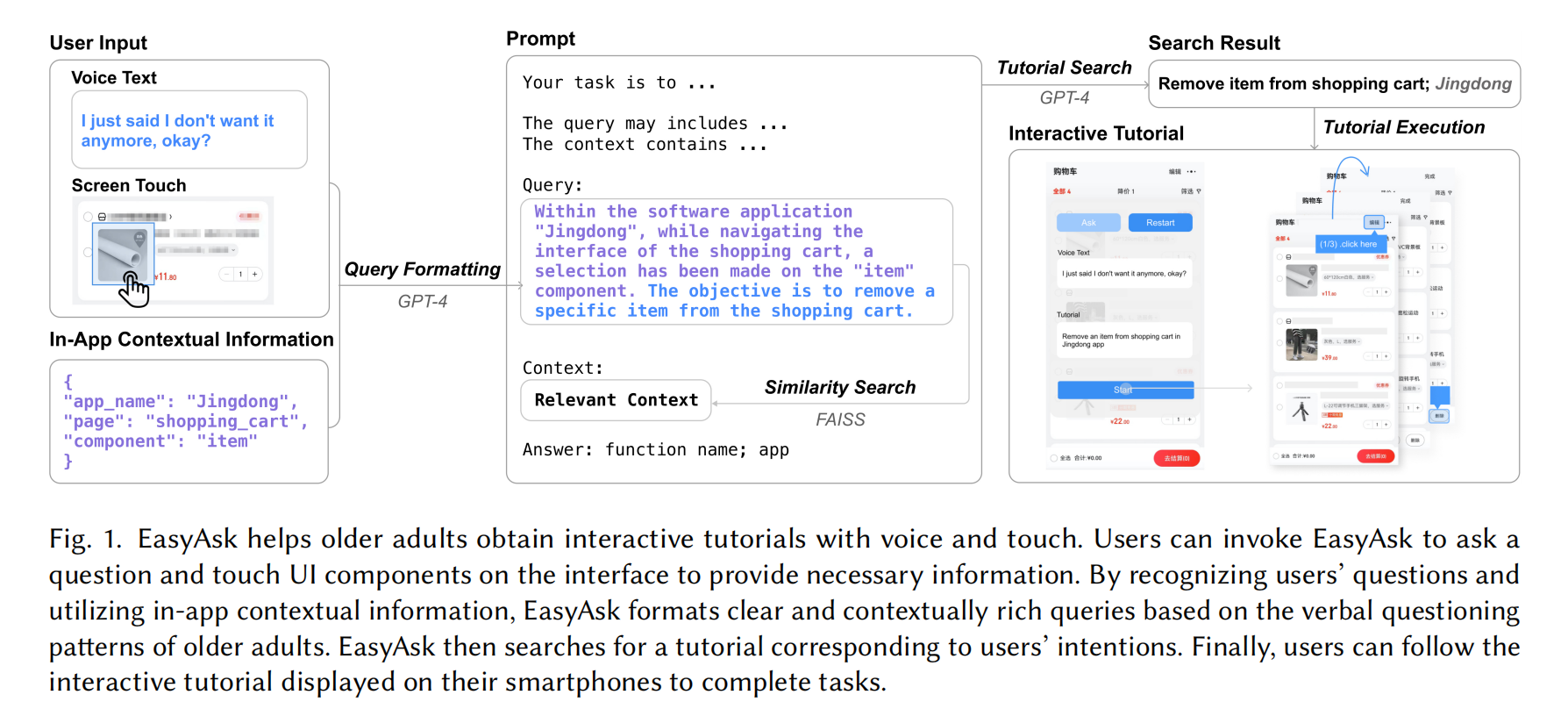
EasyAsk: An In-App Contextual Tutorial Search Assistant for Older Adults with Voice and Touch Inputs
Abstract
An easily accessible tutorial is crucial for older adults to use mobile applications (apps) on smartphones. However, older adults often struggle to search for tutorials independently and efficiently. Through a formative study, we investigated the demands of older adults in seeking assistance and identified patterns of older adults’ behaviors and verbal questions when seeking help for smartphone-related issues. Informed by the findings from the formative study, we designed EasyAsk, an app-independent method to make tutorial search accessible for older adults. This method was implemented as an Android app. Using EasyAsk, older adults can obtain interactive tutorials through voice and touch whenever they encounter problems using smartphones. To power the method, EasyAsk uses a large language model to process the voice text and contextual information provided by older adults, and another large language model to search for the tutorial. Our user experiment, involving 18 older participants, demonstrated that EasyAsk helped users obtain tutorials correctly in 98.94% of cases, making tutorial search accessible and natural.
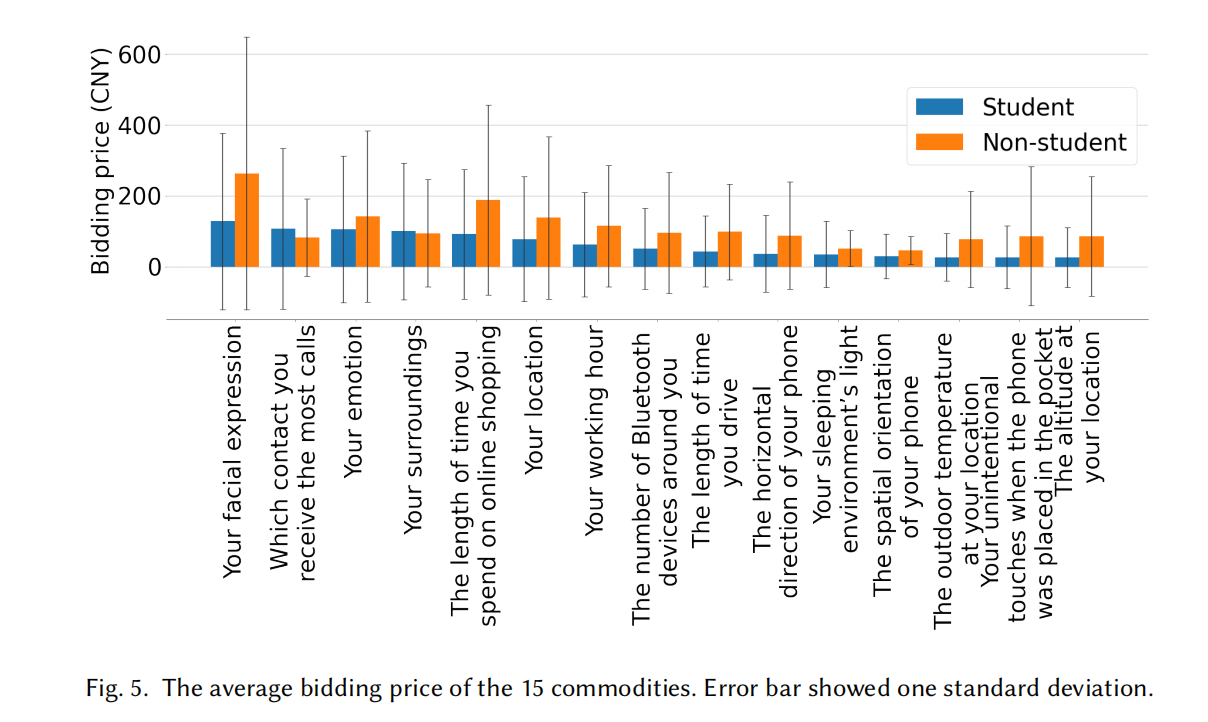
Evaluating the Privacy Valuation of Personal Data on Smartphones
Abstract
Smartphones hold a great variety of personal data during usage, which at the same time poses privacy risks. In this paper, we used the selling price to reflect users’ privacy valuation of their personal data on smartphones. In a 7-day auction, they sold their data as commodities and earn money. We first designed a total of 49 commodities with 8 attributes, covering 14 common types of personal data on smartphones. Then, through a large-scale reverse second price auction (N=181), we examined students’ valuation of 15 representative commodities. The average bid-price was 62.8 CNY (8.68 USD) and a regression model with 14 independent variables found the most influential factors for bid-price to be privacy risk, ethnic and gender. When validating our results on non-students (N=34), we found that despite they gave significantly higher prices (M=109.8 CNY, 15.17 USD), “privacy risk” was still one of the most influential factors among the 17 independent variables in the regression model. We recommended that stakeholders should provide 8 attributes of data when selling or managing it.
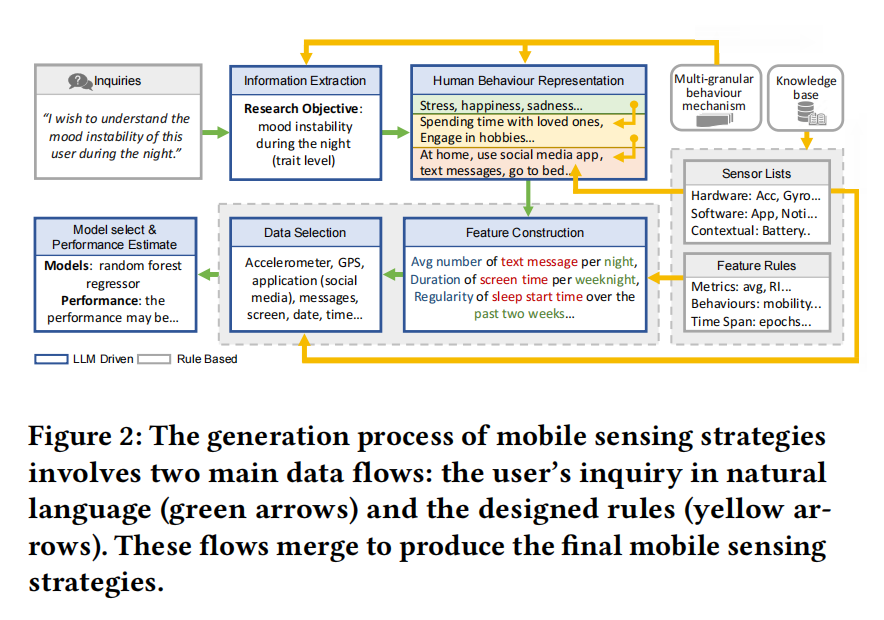
Leveraging Large Language Models for Generating Mobile Sensing Strategies in Human Behavior Modeling
Abstract
Mobile sensing plays a crucial role in generating digital traces to understand human daily lives. However, studying behaviours like mood or sleep quality in smartphone users requires carefully designed mobile sensing strategies such as sensor selection and feature construction. This process is time-consuming, burdensome, and requires expertise in multiple domains. Furthermore, the resulting sensing framework lacks generalizability, making it difficult to apply to different scenarios. In the research, we propose an automated mobile sensing strategy for human behaviour understanding. First, we establish a knowledge base and consolidate rules for data collection and effective feature construction. Then, we introduce the multi-granular human behaviour representation and design procedures for leveraging large language models to generate strategies. Our approach is validated through blind comparative studies and usability evaluation. Ultimately, our approach holds the potential to revolutionise the field of mobile sensing and its applications.
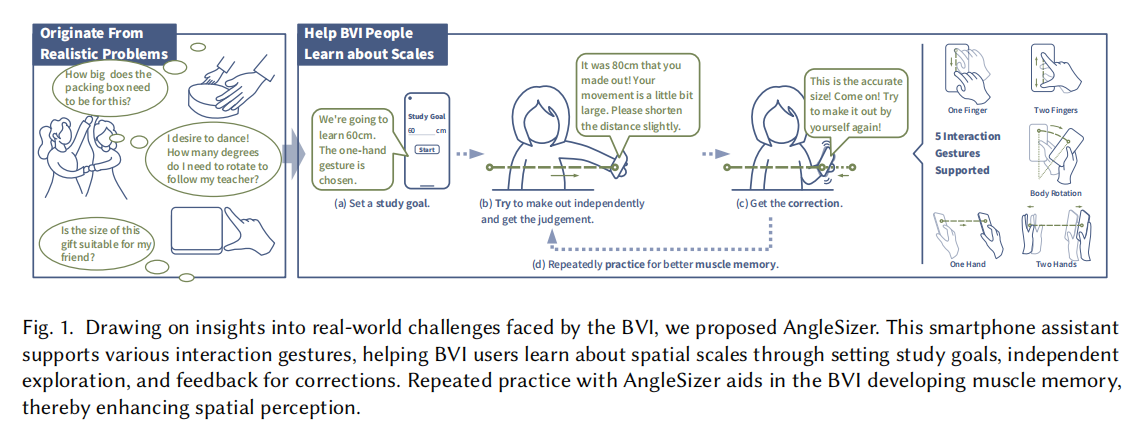
AngleSizer:Enhancing SpatialScale Perception for the Visually Impaired with an Interactive Smartphone Assistant
Abstract
Spatial perception, particularly at small and medium scales, is an essential human sense but poses a significant challenge for the blind and visually impaired (BVI). Traditional learning methods for BVI individuals are often constrained by the limited availability of suitable learning environments and high associated costs. To tackle these barriers, we conducted comprehensive studies to delve into the real-world challenges faced by the BVI community. We have identified several key factors hindering their spatial perception, including the high social cost of seeking assistance, inefficient methods of information intake, cognitive and behavioral disconnects, and a lack of opportunities for hands-on exploration. As a result, we developed AngleSizer, an innovative teaching assistant that leverages smartphone technology. AngleSizer is designed to enable BVI individuals to use natural interaction gestures to try, feel, understand, and learn about sizes and angles effectively. This tool incorporates dual vibration-audio feedback, carefully crafted teaching processes, and specialized learning modules to enhance the learning experience. Extensive user experiments validated its efficacy and applicability with diverse abilities and visual conditions. Ultimately, our research not only expands the understanding of BVI behavioral patterns but also greatly improves their spatial perception capabilities, in a way that is both cost-effective and allows for independent learning.
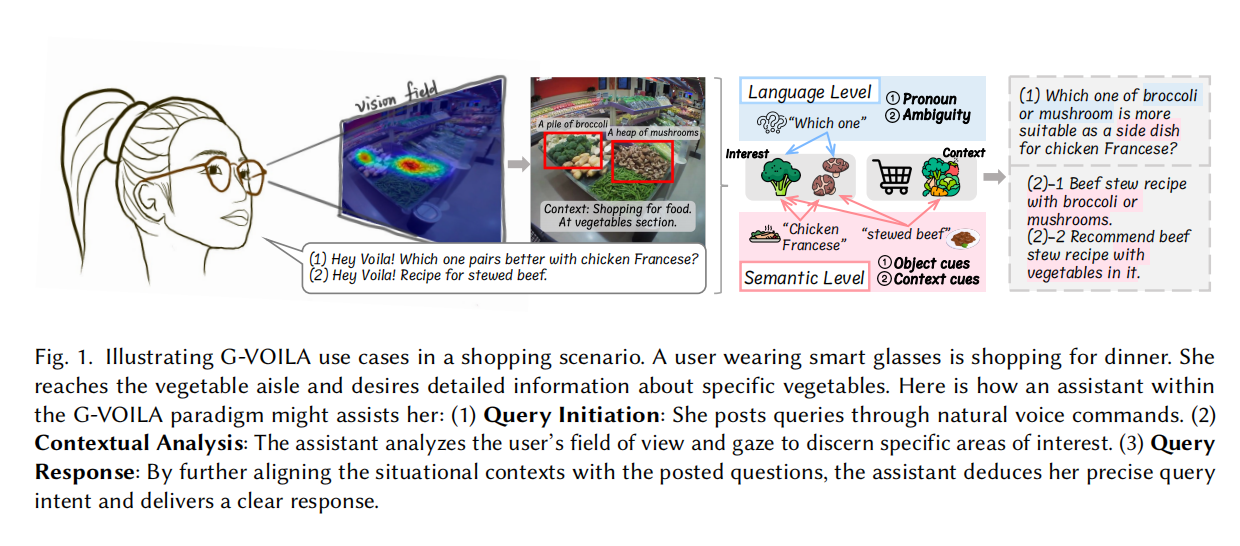
G-VOILA: Gaze-Facilitated Information Querying in Daily Scenarios
Abstract
Modern information querying systems are progressively incorporating multimodal inputs like vision and audio. However, the integration of gaze -a modality deeply linked to user intent and increasingly accessible via gaze-tracking wearables -remains under explored. This paper introduces a novel gaze-facilitated information querying paradigm, named G-VOILA, which synergizes users'gaze, visual field, and voice-based natural language queries to facilitate a more intuitive querying process.In a user-enactment study involving 21 participants in 3 daily scenarios (p=21, scene =3), we revealed the ambiguity in users'query language and a gaze-voice coordination pattern in users'natural query behaviors with G-VOILA.Based on the quantitative and qualitative findings, we developed a design framework for the G-VOILA paradigm, which effectively integrates the gaze data with the in-situ querying context.Then we implemented a G-VOILA prouf-of-concept using cutting-edge deep learning techniques.A follow-up user study (p=16, scene =2)demonstrates its effectiveness by achieving both higher objective score and subjective score, compared to a baseline without gaze data.We further conducted interviews and provided insights for future gaze-facilitated information querying systems.