论文成果 / Publications
2012
AutoWeb: automatic classification of mobile web pages for revisitation
Abstract
Revisitation in mobile Web browsers takes more time than that in desktop browsers due to the limitations of mobile phones. In this paper, we propose AutoWeb, a novel approach to speed up revisitation in mobile Web browsing. In AutoWeb, opened Web pages are automatically classified into different groups based on their contents. Users can more quickly revisit an opened Web page by narrowing down search scope into a group of pages that share the same topic. We evaluated the classification accuracy and the accuracy is 92.4%. Three experiments were conducted to investigate revisitation performance in three specific tasks. Results show AutoWeb can save significant time for revisitation by 29.5%, especially for long time Web browsing, and that it improves overall mobile Web revisitation experience. We also compare automatic classification with other revisitation methods.
Digging unintentional displacement for one-handed thumb use on touchscreen-based mobile devices
Abstract
There is usually an unaware screen distance between initial contact and final lift-off when users tap on touchscreen-based mobile devices with their fingers, which may affect users' target selection accuracy, gesture performance, etc. In this paper, we summarize such case as unintentional displacement and give its models under both static and dynamic scenarios. We then conducted two user studies to understand unintentional displacement for the widely-adopted one-handed thumb use on touchscreen-based mobile devices under both scenarios respectively. Our findings shed light on the following four questions: 1) what are the factors that affect unintentional displacement; 2) what is the distance range of the displacement; 3) how is the distance varying over time; 4) how are the unintentional points distributed around the initial contact point. These results not only explain certain touch inaccuracy, but also provide important reference for optimization and future design of UI components, gestures, input techniques, etc.
Fall Detection on Mobile Phones Using Features from a Five-Phase Model
Abstract
The injuries caused by falls are great threats to the elderly people. With the ability of communication and motion sensing, the mobile phone is an ideal platform to detect the occurrence of fall accidents and help the injured person receive first aid. However, the missed detection and false alarm of the monitoring software will cause annoyance to the users in real use. In this paper, we present a novel fall detection technique using features from a five-phase model which describes the state change of the user's motion during the fall. Experiment results validate the effectiveness of the algorithm and show that the features derived from the model as gravity-cross rate and non-primarily maximum and minimum points of the acceleration data are useful to improve the precision of the detection. Moreover, we implement the technique as uCare, an Android application that helps elderly people in fall prevention, detection and first aid seeking.
PiMarking: co-located collaborative digital annotating on large tabletops
Abstract
There are situations under which co-located people are required to perform collaborative marking tasks: for example, human resource officers need to review resumes together and teachers need to grade answer sheets after an examination. In this poster, we introduce PiMarking, a collaborative system designed to accommodate user-authenticated marking tasks and face-to-face discussions on large-scale interactive tabletop surfaces. PiMarking makes it easy for user-differentiation, document sharing and synchronized marking among group members. PiMarking puts forward user permission management mechanisms, allowing three modes for document sharing: distributed copy, share display and synchronized marking. We conducted a preliminary study using a realistic resume marking task, which proved the effectiveness of the features provided by PiMarking.
uEmergency: a collaborative system for emergency management on very large tabletop
Abstract
The vertical display, indirect input and distant communication in traditional Emergency Management Information System provide unintuitive human-computer-interaction, and thus reduce the efficiency of decision-making. This paper presents uEmergency, a multi-user collaborative system for emergency management on very large-scale interactive tabletop. It allows people to carry out face-to-face communication based on a horizontal global map. Real-time situation can be browsed and analyzed directly using their fingers and digital pens. In this paper, we also present the results of a study where two groups carried out a task for fighting forest fire based on this system. The results suggest that uEmergency can effectively help people manipulate objects, analyze situation and collaborate for coping with an emergency.
FloTree: a multi-touch interactive simulation of evolutionary processes
Abstract
We present FloTree, a multi-user simulation that illustrates key dynamic processes underlying evolutionary change. Our intention is to create a informal learning environment that links micro-level evolutionary processes to macro-level outcomes of speciation and biodiversity. On a multi-touch table, the simulation represents change from generation to generation in a population of organisms. By placing hands or arms on the surface, visitors can add environmental barriers, thus interrupting the genetic flow between the separated populations. This results in sub-populations that accumulate genetic differences independently over time, sometimes leading to the formation of new species. Learners can morph the result of the simulation into a corresponding phylogenetic tree. The free-form hand and body touch gestures invite creative input from users, encourages social interaction, and provides an opportunity for deep engagement.
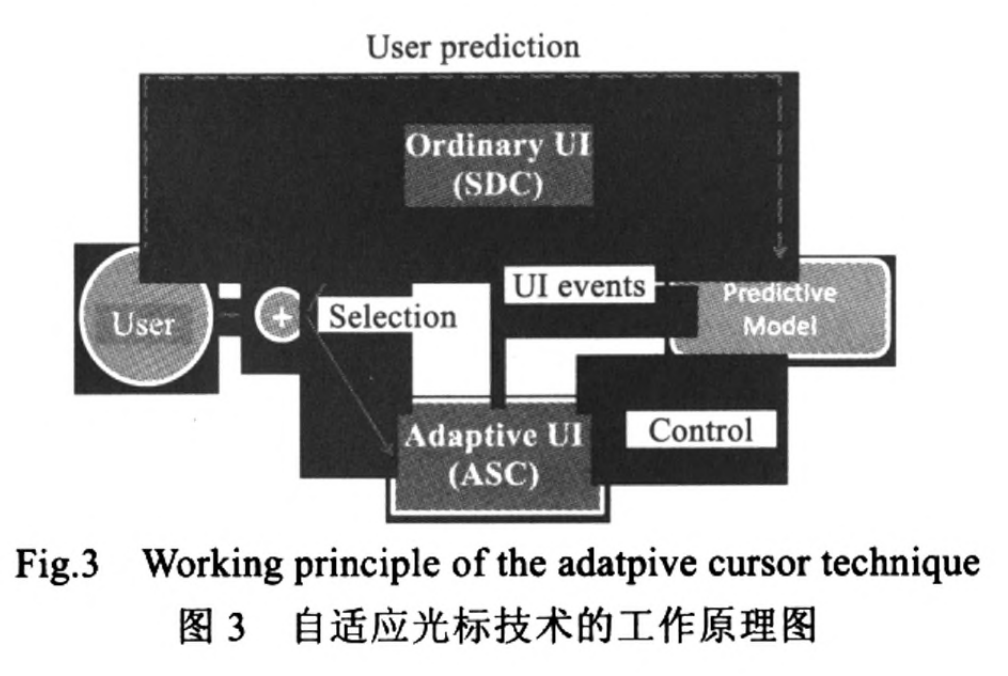
软件学报|基于自适应光标的图形用户界面输入效率优化
Abstract
提高图形用户界面(graphical user interface)的输入效率,是人机交互中的一项重要研究内容。已有的研究包括点击增强技术和自适应界面技术,前者改变光标的控制方式或呈现方式,后者改变界面上控件的位置布局,但两种技术都存在不足。通过分析界面操作,提出了图形用户界面输入效率的评价模型;然后,在此基础上提出一种人机交互效率优化技术∶自适应光标,它以自适应的方式。有选择地对界面上用户可能访问的控件通过点击增强技术支持,实现快速访问。该方法既解决了以往的自适应界面技术因频繁调整控件布局而给用户带来额外认知成本的问题,也克服了点击增强技术仅适用于稀疏控件布局的限制。为了检验其可用性,在控件较多的 Visual Studio 上实现了自适应光标技术。实验结果表明,使用自适应光标技术可以将获取目标的时间缩短27.7%,显著提高了图形用户界面的输入效率。
2011
RegionalSliding: enhancing target selection on touchscreen-based mobile devices
Abstract
Target selection on mobile devices with touchscreens usually gets users into trouble due to the occlusion of the target by the user's finger and ambiguity about which part of the finger generates the result point. In this paper, we propose a novel technique to enhance target selection on touchscreen-based mobile devices, named RegionalSliding, which selectively renders the initially "selected" target as well as its "surrounding" targets in a non-occluded area when users press down on the screen and enables users to complete the selection with sliding gestures according to the visual feedback from the rendered area. A preliminary user study shows that RegionalSliding increases the selection accuracy and brings good user experience.
Enabling Efficient Browsing and Manipulation of Web Tables on Smartphone
Abstract
Tables are very important carriers of the vast information on the Internet and are widely used in web pages. However, most designs of web tables are only for desktop PCs and just focus on how to visually and logically show large amount of data without considering their visual effects on small-screen devices. Therefore, users suffer inconvenience when browsing web tables on smartphone. In this paper, we propose to enable efficient browsing and manipulation of web tables on smartphone in order to solve the problems of both information retrieval and content replication from web tables. We implemented a mobile web browser on Android 2.1 platform, which deals with web tables in three steps: genuine table detection, table understanding and user interface design. We conducted a user study to test the effects that users used such tool. Experimental results show that the tool increases users’ browsing efficiency of web tables and the novel browsing and manipulation modes are well accepted by users.