论文成果 / Publications
2014
Enhancing Collaboration in Competitive Games in Multi-Display Environment
Abstract
In the Multi-Display Environment (MDE), we introduce a mechanism containing private, public and group workspaces for a computer-mediated tabletop board game through combination of the tabletop and mobile phones. It can sustain the important sociality between players while ensuring privacy and enhancing visual effect. Based on the popular board game Monopoly, we design Copoly on a multi-touch tabletop and mobile phones where players can form groups for collaboration. We explore the patterns of collaboration and its effect on tabletop game experience. Results show that social bonding play an important role on the frequency and patterns of collaboration in tabletop games, and players gain a more joyful experience through both competition and collaboration.
Defining and Analyzing a Gesture Set for Interactive TV Remote on Touchscreen Phones
Abstract
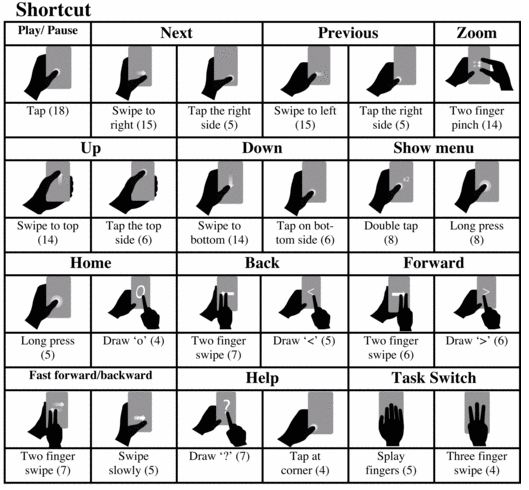
In this paper, we recruited 20 participants preforming user-defined gestures on a touch screen phone for 22 TV remote commands. Totally 440 gestures were recorded, analyzed and paired with think-aloud data for these 22 referents. After analyzing these gestures according to extended taxonomy of surface gestures and agreement measure, we presented a user-defined gesture set for interactive TV remote on touch screen phones. Despite the insight of mental models and analysis of gesture set, our findings indicate that people prefer using single-handed thumb and also prefer eyes-free gestures that need no attention switch under TV viewing scenario. Multi-display is useful in text entry and menu access tasks. Our results will contribute to better gesture design in the field of interaction between TVs and touchable mobile phones.
AirFlow: designing immersive breathing training games for COPD
Abstract
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) refers to a collection of lung diseases that result in breathing difficulties. In some cases, the symptoms of COPD can be reduced, by engaging in breathing exercises. Technology can support, and we are developing AirFlow, a suite of interactive computer games, to guide breathing exercises and promote learning. To establish requirements, we interviewed 20 people with COPD, in China, to understand their use of breathing exercises, and learn how technology might fit their lifestyle. The findings informed our design goals. We outline a prototype system, where respiration rate, waveform, and amplitude are captured and used to control a virtual environment. The system will guide users through breathing exercises, and provide training instructions, using a series of games. The immersive environment aims to support a fun and motivating experience, therefore underpinning user confidence.
uStitchHub: Stitching Multi-Touch Trajectories on Tiled Very Large Tabletops
Abstract
It is common to tile normal sized units together to obtain very large tabletops or interactive digital walls. Usually cameras are adopted to capture the touch input on the surface, which demands for fusing several multi-touch input feeds into a single feed in real time. Common approaches of stitching camera frames into aggregate images do not scale to larger number of cameras. We present uStitch Hub to address these challenges, which is specifically applied in the tabletop domain. It is a fusion mediator which accept detected blobs from multiple cameras that do and don't have overlapped field of view, remapping blobs to the dimension of the entire large tabletop, match blobs with real touches on the surface, and concatenate touch trajectories which are performed over two or more units. We conducted laboratory evaluation of uStitch Hub on its stitching success rate and as well as latency. The results prove that uStitch Hub processes fast and provides not only good stitch on touch trajectories but also low latency.
Video avatar-based remote video collaboration
Abstract
Most existing remote video communication systems are confined to how to accurately deliver adequate information in real time, but lose sight of communicators' interaction demands. Meanwhile, traditional 2D-based video communications cannot make full use of people's 3D information, which shows great potential for video communication to achieve immersive, natural and efficient interactions with 3D technique. To enhance the immersion sense and expand interaction modes in video collaboration, the design goal for ‘immersive' video communication systems was proposed and a novel, avatar-based remote video collaboration system was designed and implemented. Specifically, using Creative Senz3D depth camera, the proposed system extracted people's foreground images through background segmentation as their video avatars, and located the avatars together in a common virtual scenario. Natural and immersive interactions among people and between people and virtual scenes were also well designed, which expanded modes of interaction and collaboration in video communication. Finally, a user study was conducted and the result indicates that the proposed video avatar-based remote video cooperation mode can effectively enhance people's sense of immersion in telecommunication.
2013
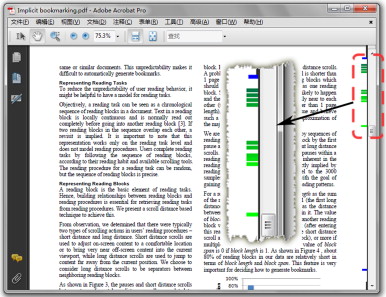
Implicit bookmarking: Improving support for revisitation in within-document reading tasks
Abstract
We explore improving support for revisitation in documents by automatically generating bookmarks based on users' reading history. After showing that dwell time and number of visits are not appropriate for predicting revisitations in documents, we model the high-level reading task as a sequence of reading blocks and recognize long-distance scrolls as separators between them. A long-distance scroll is defined as a continuous scrolling action which causes the document to be navigated beyond a one-page distance. We propose a new technique, called the Head–Tail (HT) algorithm, to generate bookmarks at the head and the tail of reading blocks, whose validity is quantitatively verified by log data analysis. Two studies were conducted to investigate this HT implicit bookmarking technique. The first is a controlled experiment that compared the HT algorithm to the widely used simple recency algorithm for generating implicit bookmarks, in terms of revisit coverage ability and distance between bookmarks ...
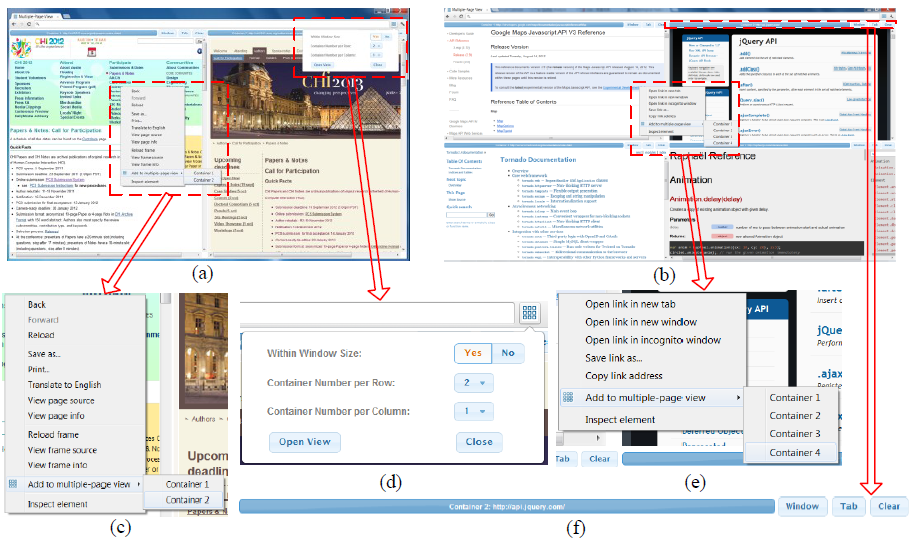
Facilitating parallel web browsing through multiple-page view
Abstract
Parallel web browsing describes the behavior where users visit web pages in multiple concurrent threads. Qualitative studies have observed this activity being performed with multiple browser windows or tabs. However, these solutions are not satisfying since a large amount of time is wasted on switch among windows and tabs. In this paper, we propose the multiple-page view to facilitate parallel web browsing. Specifically, we provide users with the experience of visiting multiple web pages in one browser window and tab with extensions of prevalent desktop web browsers. Through user study and survey, we found that 2-4 pages within the window size were preferred for multiple-page view in spite of the diverse screen sizes and resolutions. Analytical results of logs from the user study also showed an improvement of 26.3% in users' efficiency of performing parallel web browsing tasks, compared to traditional browsing with multiple windows or tabs.
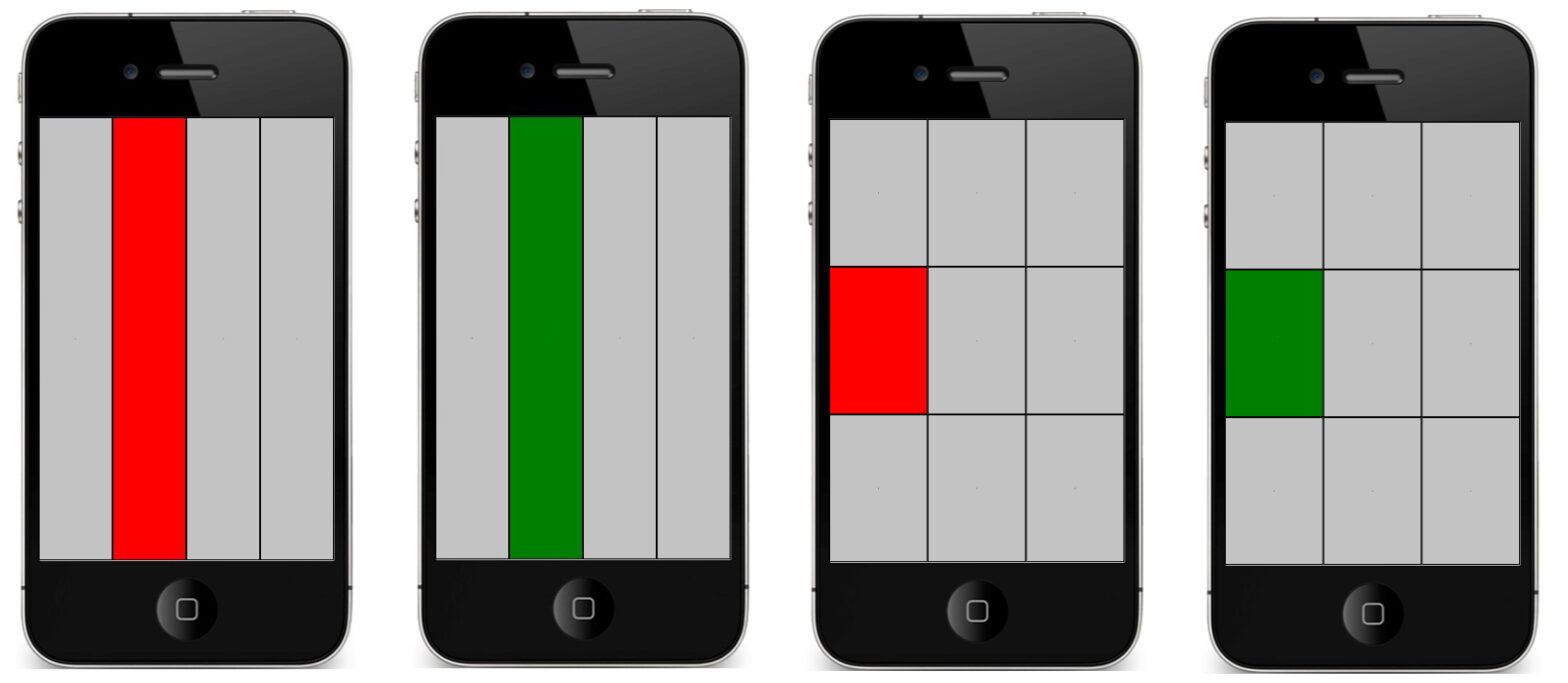
Understanding performance of eyes-free, absolute position control on touchable mobile phones
Abstract
Many eyes-free interaction techniques have been proposed for touchscreens, but few researches have studied human's eyes-free pointing ability with mobile phones. In this paper, we investigate the single-handed thumb performance of eyes-free, absolute position control on mobile touch screens. Both 1D and 2D experiments were conducted. We explored the effects of target size and location on eyes-free touch patterns and accuracy. Our findings show that variance of touch points per target will converge as target size decreases. The centroid of touch points per target tends to be offset to the left of target center along horizontal direction, and shift toward screen center along vertical direction. Average accuracy drops from 99.6% of 2*2 layout to 85.0% of 4*4 layout, and average per target varies depending on the location of target. Our findings and design implications provide a foundation for future researches based on eyes-free, absolute position control using thumb on mobile devices.
QOOK: a new physical-virtual coupling experience for active reading
Abstract
We present QOOK, an interactive reading system that incorporates the benefits of both physical and digital books to facilitate active reading. QOOK uses a top-projector to create digital contents on a blank paper book. By detecting markers attached to each page, QOOK allows users to flip pages just like they would with a real book. Electronic functions such as keyword searching, highlighting and bookmarking are included to provide users with additional digital assistance. With a Kinect sensor that recognizes touch gestures, QOOK enables people to use these electronic functions directly with their fingers. The combination of the electronic functions of the virtual interface and free-form interaction with the physical book creates a natural reading experience, providing an opportunity for faster navigation between pages and better understanding of the book contents.